[GSP141] Creating an Object Detection Application Using TensorFlow
https://www.qwiklabs.com/focuses/1823?parent=catalog
This lab will show you how to install and run an object detection application. The application uses TensorFlow and other public API libraries to detect multiple objects in an uploaded image.
Objectives
This is a basic lab designed to familiarize you with TensorFlow applications. When you are finished, you should be able to:
- Create a virtual machine (VM) using Google Compute Engine.
- Install the Object Detection API library.
- Install and launch an object detection web application.
- Test the web application with uploaded images.
TensorFlow architecture overview
The object detection application uses the following components:
-
TensorFlow: An open source machine learning library developed by researchers and engineers within Google’s Machine Intelligence research organization. TensorFlow runs on multiple computers to distribute the training workloads.
-
Object Detection API: An open source framework built on top of TensorFlow that makes it easy to construct, train, and deploy object detection models.
-
Pre-trained object detection models: The Object Detection API provides pre-trained object detection models for users running inference jobs. Users are not required to train models from scratch.
Local implementation
The following diagram shows how this Qwiklab is implemented. The web application is deployed to a VM instance running on Compute Engine.
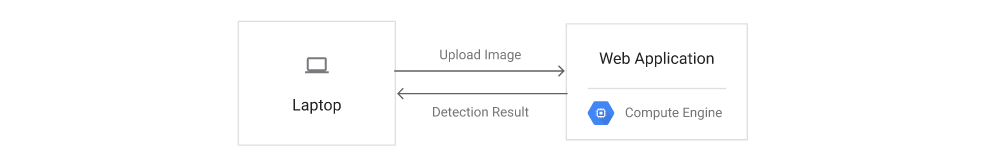
When the client uploads an image to the application, the application runs the inference job locally. The pre-trained model returns the labels of detected objects, and the image coordinates of the corresponding objects. Using these values, the application generates new images populated with rectangles around the detected objects. Separate images are generated for each object category, allowing the client to discriminate between selected objects.
Remote implementation
You can deploy the pre-trained model on Google Cloud Machine Learning Engine to provide an API service for inference. If you do, the web application sends an API request to detect objects in the uploaded image, instead of running the inference job locally.
TensorFlow allows you to choose which platform to execute inference jobs on depending on your business needs. This flexibility shows the advantage of Google Cloud Platform and TensorFlow as an open platform for machine learning.
Pre-trained models
You can use five pre-trained models with the Object Detection API. They are trained with the COCO dataset and are capable of detecting general objects in 80 categories.
The COCO mAP column shows the model’s accuracy index. Higher numbers indicate better accuracy. As speed increases, accuracy decreases.
Launch a VM instance
Products and Services > Compute Engine > VM Instances > Create
Machine type - 4 vCPUs. In the Machine type section, click the Customize link. Memory - replace 30 with 8.
Firewall > Allow HTTP traffic.
Click the Management, disks, networking, SSH keys link, then click the Networking tab.
Click the pencil icon next to the default row in the Network interfaces section.
In the External IP dropdown, select Create IP address from to assign a static IP address.
Type staticip in the Name field, then click Reserve. Click the Create button to create the instance and wait for the instance to be created.
GCP console > Compute Engine > VM instances > Instance-1 > SSH
Install the Object Detection API library
$ sudo su -
# apt -y update && apt -y upgrade
# apt-get install -y protobuf-compiler python-pil python-lxml python-pip python-dev git
$ pip install Flask==0.12.2 WTForms==2.1 Flask_WTF==0.14.2 Werkzeug==0.12.2
$ pip install --upgrade https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/linux/cpu/tensorflow-1.1.0-cp27-none-linux_x86_64.whl
# cd /opt
# git clone https://github.com/tensorflow/models
# cd models/research
# protoc object_detection/protos/*.proto --python_out=.
Download the pre-trained model binaries by running the following commands:
# mkdir -p /opt/graph_def
# cd /tmp
# for model in \
ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco_11_06_2017 \
ssd_inception_v2_coco_11_06_2017 \
rfcn_resnet101_coco_11_06_2017 \
faster_rcnn_resnet101_coco_11_06_2017 \
faster_rcnn_inception_resnet_v2_atrous_coco_11_06_2017
do \
curl -OL http://download.tensorflow.org/models/object_detection/$model.tar.gz
tar -xzf $model.tar.gz $model/frozen_inference_graph.pb
cp -a $model /opt/graph_def/
done
Now you will choose a model for the web application to use. For this lab, enter the following command faster_rcnn_resnet101_coco_11_06_2017:
# ln -sf /opt/graph_def/faster_rcnn_resnet101_coco_11_06_2017/frozen_inference_graph.pb /opt/graph_def/frozen_inference_graph.pb
Install and launch the web application
# cd $HOME
# git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/tensorflow-object-detection-example
# cp -a tensorflow-object-detection-example/object_detection_app /opt/
# cp /opt/object_detection_app/object-detection.service /etc/systemd/system/
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl enable object-detection
# systemctl start object-detection
# systemctl status object-detection
The application loads the model binary immediately after launch. It will take a minute to start serving requests from clients. You’ll see the message Running on http://0.0.0.0:80/ (Press CTRL+C to quit) when it’s ready.
Return to the Google Cloud Platform console tab.
Click the external ip-address link next to your VM instance to open a browser window to the example application.
Log in with the following credentials:
Username - username Password - passw0rd
Click Choose File and select an image file from your computer to analyse.
Click Upload to test.
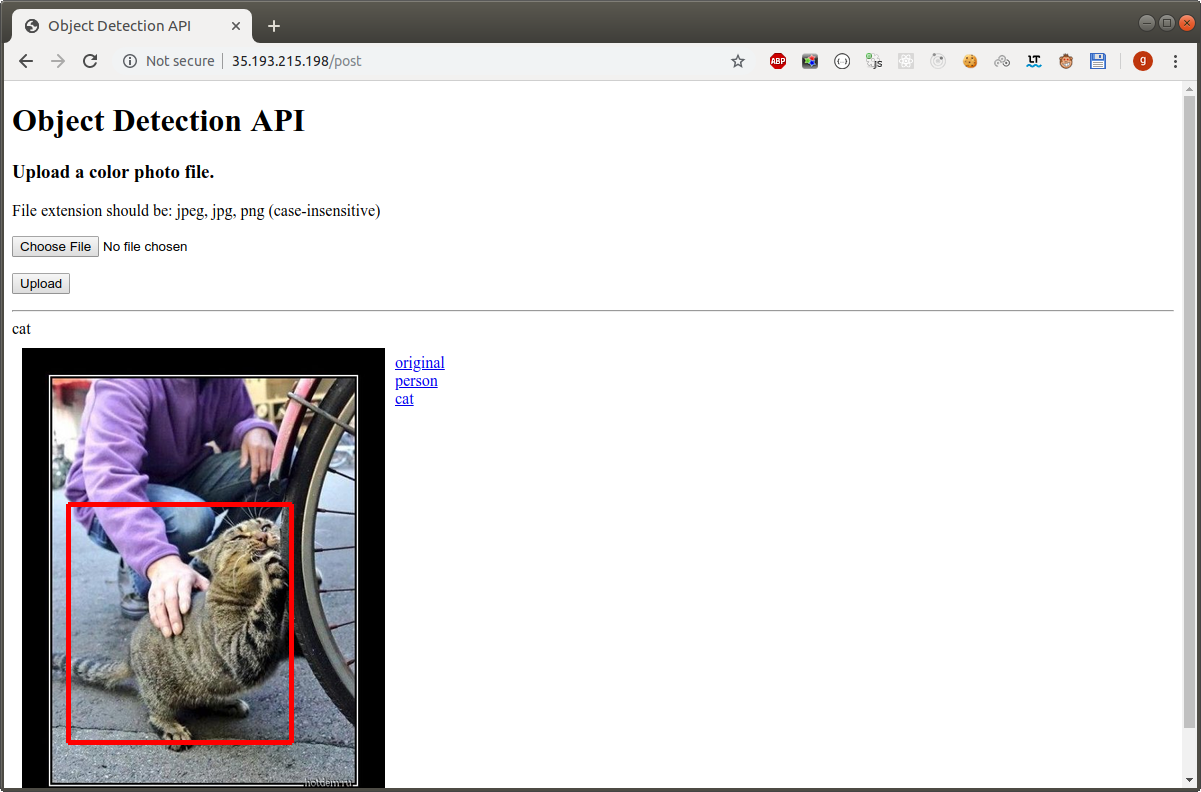
When you upload an image file with a JPEG, JPG, or PNG extension, the application shows the result of the object detection inference, as shown in the following image. The inference might take up to 30 seconds, depending on the image.
The object names detected by the model are shown to the right of the image, in the application window. Click an object name to display rectangles surrounding the corresponding objects in the image. The rectangle thickness increases with object identification confidence.
In the above image, “fork”, “cup”, “dining table”, “person”, and “knife”, are detected. After clicking “cup”, rectangles display around all detected cups in the image. Click “original” to see the original image.
Optional: If you have time, test this model’s accuracy by uploading images that contain different types of objects.
Change the inference model
$ systemctl stop object-detection
Replace [MODEL NAME] with one of the following options.
- ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco_11_06_2017
- ssd_inception_v2_coco_11_06_2017
- rfcn_resnet101_coco_11_06_2017
- faster_rcnn_resnet101_coco_11_06_2017
-
faster_rcnn_inception_resnet_v2_atrous_coco_11_06_2017
# ln -sf /opt/graph_def/[MODEL NAME]/frozen_inference_graph.pb /opt/graph_def/frozen_inference_graph.pb
# systemctl start object-detection
Once the application has successfully re-started with the updated model, retest some of your images to see how change affects object detection.