[GSP138] Scanning User-generated Content Using the Cloud Video Intelligence and Cloud Vision APIs
https://www.qwiklabs.com/focuses/1831?parent=catalog
This lab will show you how to deploy a set of Cloud Functions in order to process images and videos with the Cloud Vision API and Cloud Video Intelligence API.
Social marketing campaigns often invite consumers to submit user-generated images and videos. Campaigns that solicit videos and images often use them for contest submissions, product testimonials, or as user-generated content for public campaign websites. Processing these submissions at scale requires considerable resources.
The Cloud Video Intelligence and Cloud Vision APIs offer you a scalable and serverless way to implement intelligent image and video filtering, accelerating submission processing. If you use the safe-search feature in the Vision API solution and the explicit content detection feature in the Video Intelligence API, you can eliminate images and videos that are identified as unsafe or undesirable content before further processing.
Objectives
- Deploy four Cloud Functions.
- Create the supporting Cloud Storage buckets, Cloud Pub/Sub topics, and Cloud Storage Pub/Sub Notifications.
- Create the supporting BigQuery dataset and table.
Requirements
You’ll need image and video files that you can upload into the lab for analysis. Ideally they would be of different types - with people whose faces can be seen, no people, landscape, close-ups - so you can see how the image analysis treats the image. You can also just use a single image or video.
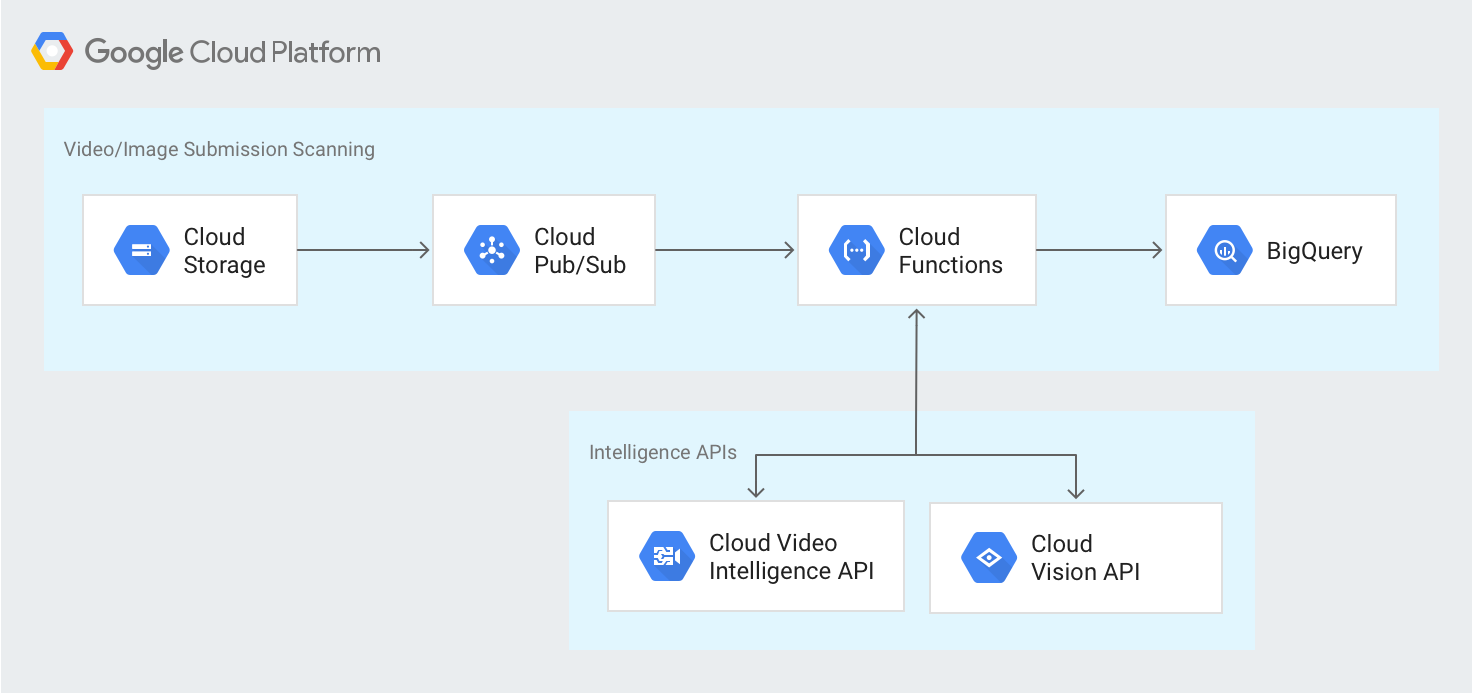
Architecture
The following diagram outlines the high-level architecture:
Initializing your Environment
Prepare for the lab by setting up some environment variables that you’ll need in the lab.
$ export PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud info --format='value(config.project)')
$ export IV_BUCKET_NAME=${PROJECT_ID}-upload
$ export FILTERED_BUCKET_NAME=${PROJECT_ID}-filtered
$ export FLAGGED_BUCKET_NAME=${PROJECT_ID}-flagged
$ export STAGING_BUCKET_NAME=${PROJECT_ID}-staging
Creating Cloud Storage buckets
Cloud Storage buckets provide a storage location for uploading your images and videos. Now you will create four different Cloud Storage buckets.
Create a bucket for storing your uploaded images and video files using the IV_BUCKET_NAME environment variable:
$ gsutil mb gs://${IV_BUCKET_NAME}
Create a bucket for storing your filtered image and video files using the FILTERED_BUCKET_NAME environment variable:
$ gsutil mb gs://${FILTERED_BUCKET_NAME}
Create a bucket for storing your flagged image and video files using the FLAGGED_BUCKET_NAME environment variable:
$ gsutil mb gs://${FLAGGED_BUCKET_NAME}
Create a bucket for your Cloud Functions to use as a staging location using the STAGING_BUCKET_NAME environment variable:
$ gsutil mb gs://${STAGING_BUCKET_NAME}
Check that the four storage buckets have been created.
$ gsutil ls
gs://qwiklabs-gcp-d2118b2986e3ccd7-filtered/
gs://qwiklabs-gcp-d2118b2986e3ccd7-flagged/
gs://qwiklabs-gcp-d2118b2986e3ccd7-staging/
gs://qwiklabs-gcp-d2118b2986e3ccd7-upload/
Creating Cloud Pub/Sub topics
Cloud Pub/Sub topics is used for Cloud Storage notification messages and for messages between your Cloud Functions. This lab has some of the topic names preset to specific defaults which are used in this section for the topic names.
Create a topic to receive Cloud Storage notifications whenever one of your files is uploaded to Cloud Storage. You set the default value to upload_notification and save it in an environment variable since it will be used later:
$ export UPLOAD_NOTIFICATION_TOPIC=upload_notification
$ gcloud pubsub topics create ${UPLOAD_NOTIFICATION_TOPIC}
Create a topic to receive your messages from the Vision API. The default value in the config.json file is visionapiservice:
$ gcloud pubsub topics create visionapiservice
next create a topic to receive your messages from the Video Intelligence API. The default value in the config.json file is videointelligenceservice.
$ gcloud pubsub topics create videointelligenceservice
Create a topic to receive your messages to store in BigQuery. The default value in the config.json file is bqinsert:
$ gcloud pubsub topics create bqinsert
Check that the four pubsub topics have been created:
$ gcloud pubsub topics list
---
name: projects/qwiklabs-gcp-d2118b2986e3ccd7/topics/videointelligenceservice
---
name: projects/qwiklabs-gcp-d2118b2986e3ccd7/topics/bqinsert
---
name: projects/qwiklabs-gcp-d2118b2986e3ccd7/topics/upload_notification
---
name: projects/qwiklabs-gcp-d2118b2986e3ccd7/topics/visionapiservice
Creating Cloud Storage notifications
Create a notification that is triggered only when one of your new objects is placed in the Cloud Storage file upload bucket:
$ gsutil notification create -t upload_notification -f json -e OBJECT_FINALIZE gs://${IV_BUCKET_NAME}
Confirm that your notification has been created for the bucket:
$ gsutil notification list gs://${IV_BUCKET_NAME}
You’ll see this output, if the function succeeds:
Filters: Event Types: OBJECT_FINALIZE
Preparing the Cloud Functions for Deployment
The code for the cloud functions used in this lab are available on GitHub, defined in the index.js file. You can examine the source in detail here to see how each of the functions is implemented.
Download the code from GitHub using the following command:
$ git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/cloud-functions-intelligentcontent-nodejs
$ cd cloud-functions-intelligentcontent-nodejs
Create the BigQuery dataset and table
The results of the Vision and Video Intelligence APIs are stored in BigQuery. The demo solution used in this Qwiklab has default dataset and table names set to intelligentcontentfilter and filtered_content. You can change these values, but if you do you must also make those changes in the config.json file that is downloaded later as part of the solution.
Create your BigQuery dataset:
$ export DATASET_ID=intelligentcontentfilter
$ export TABLE_NAME=filtered_content
$ bq --project_id ${PROJECT_ID} mk ${DATASET_ID}
The dataset name is set to intelligentcontentfilter to match the default value in the config.json file.
Now you’ll create your BigQuery table from the schema file that is included with the lab. The dataset and table name is set to filtered_content to match the default values in the config.json file and the schema is defined in the file intelligent_content_bq_schema.json.
Run the following to create the BigQuery table:
$ bq --project_id ${PROJECT_ID} mk --schema intelligent_content_bq_schema.json -t ${DATASET_ID}.${TABLE_NAME}
Verify that your BigQuery table has been created by running:
$ bq --project_id ${PROJECT_ID} show ${DATASET_ID}.${TABLE_NAME}
Table qwiklabs-gcp-d2118b2986e3ccd7:intelligentcontentfilter.filtered_content
Last modified Schema Total Rows Total Bytes Expiration Time Partitioning Labels
----------------- ------------------------------------------ ------------ ------------- ------------ ------------------- --------
19 Jun 21:34:51 |- gcsUrl: string (required) 0 0
|- contentUrl: string (required)
|- contentType: string (required)
|- insertTimestamp: timestamp (required)
+- labels: record (repeated)
| |- name: string
+- safeSearch: record (repeated)
| |- flaggedType: string
| |- likelihood: string
Edit your JSON configuration file
Before you can deploy the cloud functions defined in the source code, you must modify the config.json file to use your specific Cloud Storage buckets, Cloud Pub/Sub topic names, and BigQuery dataset ID and table name.
$ sed -i "s/\[PROJECT-ID\]/$PROJECT_ID/g" config.json
$ sed -i "s/\[FLAGGED_BUCKET_NAME\]/$FLAGGED_BUCKET_NAME/g" config.json
$ sed -i "s/\[FILTERED_BUCKET_NAME\]/$FILTERED_BUCKET_NAME/g" config.json
$ sed -i "s/\[DATASET_ID\]/$DATASET_ID/g" config.json
$ sed -i "s/\[TABLE_NAME\]/$TABLE_NAME/g" config.json
Deploying the Cloud Functions
The code for the cloud functions used in this lab are available on GitHub, defined in the index.js file. You can examine the source in detail here to see how each of the functions is implemented. The deployments can each take a few minutes to complete.
Deploy the GCStoPubsub function
Next you will deploy the GCStoPubsub Cloud Function, which contains the logic to receive a Cloud Storage notification message from Cloud Pub/Sub and forward the message to the appropriate function with another Cloud Pub/Sub message.
$ gcloud functions deploy GCStoPubsub --runtime nodejs6 --stage-bucket gs://${STAGING_BUCKET_NAME} --trigger-topic ${UPLOAD_NOTIFICATION_TOPIC} --entry-point GCStoPubsub
Type “Y” when asked to Allow unauthenticated invocations of new function [GCStoPubsub]?
Deploy the visionAPI function
Deploy your visionAPI Cloud Function, which contains the logic to receive a message with Cloud Pub/Sub, call the Vision API, and forward the message to the insertIntoBigQuery Cloud Function with another Cloud Pub/Sub message. If you chose to use a different Vision API topic name then change that name here as well.
$ gcloud functions deploy visionAPI --runtime nodejs6 --stage-bucket gs://${STAGING_BUCKET_NAME} --trigger-topic visionapiservice --entry-point visionAPI
Type “Y” when asked to Allow unauthenticated invocations of new function [GCStoPubsub]?.
Deploy the videoIntelligenceAPI function
Deploy your videoIntelligenceAPI Cloud Function, which contains the logic to receive a message with Cloud Pub/Sub, call the Video Intelligence API, and forward the message to the insertIntoBigQuery Cloud Function with another Cloud Pub/Sub message. If you chose to use a different Video Intelligence API topic name then change that name here as well.
$ gcloud functions deploy videoIntelligenceAPI --runtime nodejs6 --stage-bucket gs://${STAGING_BUCKET_NAME} --trigger-topic videointelligenceservice --entry-point videoIntelligenceAPI --timeout 540
Deploy the insertIntoBigQuery function
Deploy your insertIntoBigQuery Cloud Function, which contains the logic to receive a message with Cloud Pub/Sub and call the BigQuery API to insert the data into your BigQuery table. If you chose to use a different BigQuery topic name then change that name here as well.
$ gcloud functions deploy insertIntoBigQuery --runtime nodejs6 --stage-bucket gs://${STAGING_BUCKET_NAME} --trigger-topic bqinsert --entry-point insertIntoBigQuery
Confirm that the Cloud Functions have been deployed
$ gcloud beta functions list
NAME STATUS TRIGGER REGION
GCStoPubsub ACTIVE Event Trigger us-central1
insertIntoBigQuery ACTIVE Event Trigger us-central1
videoIntelligenceAPI ACTIVE Event Trigger us-central1
visionAPI ACTIVE Event Trigger us-central1
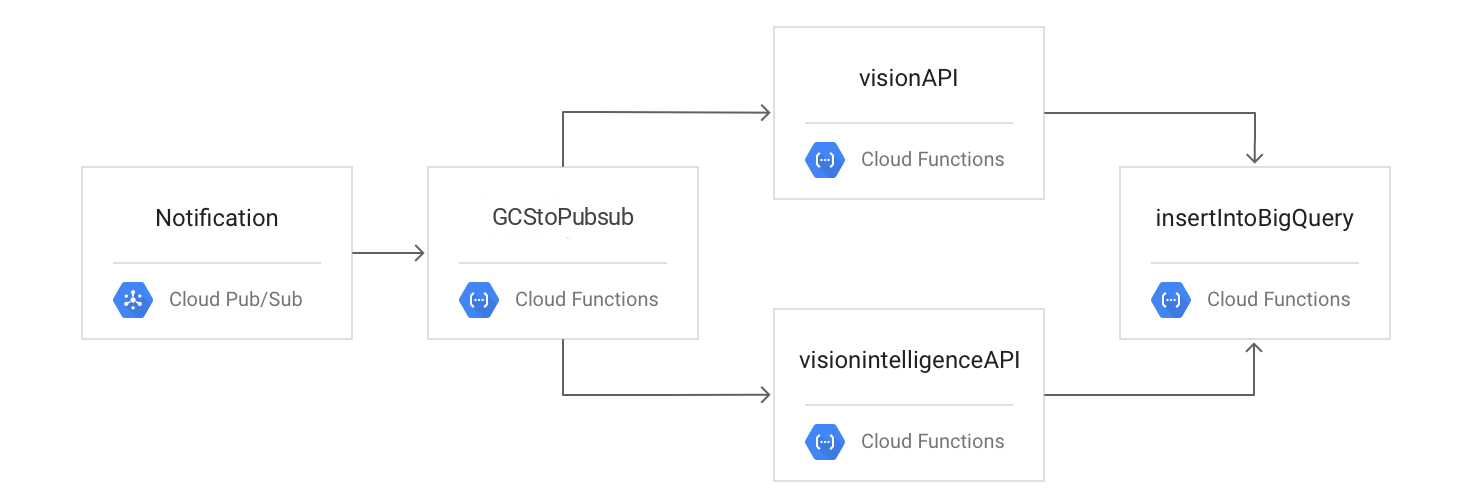
Testing the Flow
The following diagram outlines the processing flow:
You test the process by uploading your files to Cloud Storage, checking your logs, and viewing your results in BigQuery.
Upload an image and a video file to the upload storage bucket.
Google Cloud Platform Console > Storage > Browser.
Click the name of the bucket with the -upload suffix and then click Upload Files.
Upload some image files and/or video files from your local machine.
Monitor Log Activity
Switch back to the Google Cloud Shell to verify that your Cloud Functions were triggered and ran successfully by viewing the Cloud Functions logs captured in Cloud Logging:
Run the following to test GCStoPubsub:
$ gcloud beta functions logs read --filter "finished with status" "GCStoPubsub" --limit 100
Resulting output:
LEVEL NAME EXECUTION_ID TIME_UTC LOG
D GCStoPubsub 590812496668329 2019-06-19 18:49:09.884 Function execution took 2269 ms, finished with status: 'ok'
Run the following to test insertIntoBigQuery:
$ gcloud beta functions logs read --filter "finished with status" "insertIntoBigQuery" --limit 100
Resulting output:
LEVEL NAME EXECUTION_ID TIME_UTC LOG
D insertIntoBigQuery 590822806148171 2019-06-19 18:51:46.088 Function execution took 4888 ms, finished with status: 'ok'
View Results in BigQuery
To see your results in BigQuery, you’ll create SQL commands to query BigQuery.
Run the following, replacing [PROJECT_ID], [DATASET_ID], and [TABLE_NAME] with your project ID, dataset ID, and BigQuery table name if you found out that variables created for above doesn’t contain correct value:
echo "
#standardSql
SELECT insertTimestamp,
contentUrl,
flattenedSafeSearch.flaggedType,
flattenedSafeSearch.likelihood
FROM \`$PROJECT_ID.$DATASET_ID.$TABLE_NAME\`
CROSS JOIN UNNEST(safeSearch) AS flattenedSafeSearch
ORDER BY insertTimestamp DESC,
contentUrl,
flattenedSafeSearch.flaggedType
LIMIT 1000
" > sql.txt
View your BigQuery results with the following command. Replace [PROJECT_ID]with your project ID:
$ bq --project_id ${PROJECT_ID} query < sql.txt
Resulting output:
+---------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------------+------------+
| insertTimestamp | contentUrl | flaggedType | likelihood |
+---------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------------+------------+
| 2019-06-19 18:49:10 | https://storage.cloud.google.com/qwiklabs-gcp-d2118b2986e3ccd7-flagged/Домен РФ.mp4 | adult | POSSIBLE |
+---------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------------+------------+
Или тоже самое можно сделать в консоли BigQuery