[Qwiklabs] Getting Started with Blockchain on GCP using Hyperledger Fabric and Composer
https://www.qwiklabs.com/focuses/3744?catalog_rank=%7B%22rank%22%3A1%2C%22num_filters%22%3A0%2C%22has_search%22%3Atrue%7D&parent=catalog&search_id=6510491
Похоже лабораторка повторяет материал из примера.
https://hyperledger.github.io/composer/latest/tutorials/playground-tutorial.html
Может мне неповезло и облачный композер не работает именно тогда, когда он мне в первый раз понадобился?
Не смог пройти лабу. Не знаю, как задеплоить. Там нужны какие-то сертификаты.
Overview
Blockchain
A blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked using cryptography. Each block contains:
- a cryptographic hash of the previous block
- a timestamp
- transaction data (generally represented as a merkle tree root hash)
By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of the data. It is “an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way”. For use as a distributed ledger, a blockchain is typically managed by a peer-to-peer network collectively adhering to a protocol for inter-node communication and validating new blocks. Once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without alteration of all subsequent blocks, which requires consensus of the network majority. Although blockchain records are not unalterable, blockchains may be considered secure by design and exemplify a distributed computing system with high Byzantine fault tolerance. Decentralized consensus has therefore been claimed with a blockchain.
Hyperledger
Hyperledger is an open source collaborative effort created to advance cross-industry blockchain technologies. It is a global collaboration, hosted by The Linux Foundation, and includes leaders in finance, banking, Internet of Things, supply chains, manufacturing, and technology.
Hyperledger Composer
Hyperledger Composer is an extensive open development toolset and framework to make developing blockchain applications easier.
Hyperledger Composer can be used to rapidly develop use cases and deploy a blockchain solution in weeks rather than months. Hyperledger Composer allows you to model your business network and integrate existing systems and data with your blockchain applications. It supports the existing Hyperledger Fabric blockchain infrastructure and runtime, which supports pluggable blockchain consensus protocols to ensure that transactions are validated according to policy by the designated business network participants.
For an example of a business network in action; a realtor can quickly model their business network as such:
Assets: houses and listings
Participants: buyers and homeowners
Transactions: buying or selling houses, and creating and closing listings
In this lab, you will learn to use Hyperledger Composer to quickly model a business network containing assets, participants, and transactions related to them. Hyperledger Composer Playground provides a user interface for the configuration, deployment, and testing of a business network.
What you’ll learn
How to deploy Hyperledger Fabric and Composer solution from GCP Marketplace.
How to deploy a new business network.
How to use Hyperledger Composer Playground to configure and test the deployed business network by creating sample assets, participants, and transactions.
Launch Hyperledger Fabric and Composer
In this section, you will launch the Hyperledger Fabric and Composer solution available on GCP Marketplace.
-
From the Navigation menu, select Marketplace.
-
Type Hyperledger in the search box then select Hyperledger Fabric and Composer.
-
Click LAUNCH ON COMPUTE ENGINE.
You are now presented with the deployment properties setup.
-
For Deployment name, type hyperledger-fabric-and-composer.
-
Check the box to accept the Terms of Service.
-
Keep the rest of the settings at their defaults and click Deploy.
This solution will be deployed by Deployment Manager and you can watch the progress on the Deployment Manager screen, which is the screen you’re on.
- Once the solution is deployed, from the Navigation menu, select Compute Engine.
You should see a VM instance that was created as part of the deployment.
-
Click on the instance name to open the VM instance details page.
-
Click EDIT at the top.
-
Scroll down to Network tags and enter hyperledgerin the field.
This will allow you to configure specific firewall rules on instances which have been tagged with the Network tag - hyperledger. You will configure this in the next section.
- Click Save.
Enable firewall access on the VM
To access Playground, you will need to enable port 8080 on the deployed VM. For security purposes, you will create a firewall rule that allows access to port 8080 only from your browser IP.
-
Open a new browser tab and navigate to http://www.whatismyip.com.
-
Copy the public IPv4 address.
-
In the Console, go to Navigation menu > VPC network > Firewall rules.
-
Click CREATE FIREWALL RULE.
-
Name for the firewall rule hyperleger-firewall-rule and add an optional description.
-
Under Targets, ensure that the Specified target tags option is selected.
-
For Target tags, enter the Network tag name that you created in the previous section, hyperledger.
-
Under Source filter, select IP ranges.
-
For Source IP ranges, enter your public IPv4 address with the mask /32.
For example, if your public IPv4 address is 104.132.25.98, enter the range as 104.132.25.98/32.
- Under Protocols and ports, select the Specified protocols and ports option.
a. Check the tcp checkbox b. Enter the port number in the tcp box as 8080
Note: This is the port number on which Hyperledger Composer will be listening by default.
- Click Create. Wait for the firewall rule to be created before moving on.
Deploy and access Hyperledger Composer Playground
-
From the Navigation menu, select Compute Engine.
-
Click the SSH button for the Hyperledger VM.
-
Inside the SSH session, run the following command to run as root:
sudo su -
Deploy Composer Playground by running:
composer-playground
This will deploy the Playground solution and run it on port 8080 by default.
-
Go back to the Console and copy the External IP of the Hyperledger VM.
-
Open a new browser tab and navigate to http://
:8080 to access Hyperledger Composer Playground. -
Click the Let’s Blockchain! button to get started.
Using Playground
In this section, you will set up a business network, defining assets, participants and transactions, and testing the network by creating some participants, an asset, and submitting transactions to change the ownership of the asset from one to another.
Create and connect to a new business network
A business network has a couple of defining properties; a name, and an optional description. You can also choose to base a new business network on an existing template, or import your own template. This represents the different components of the business network:
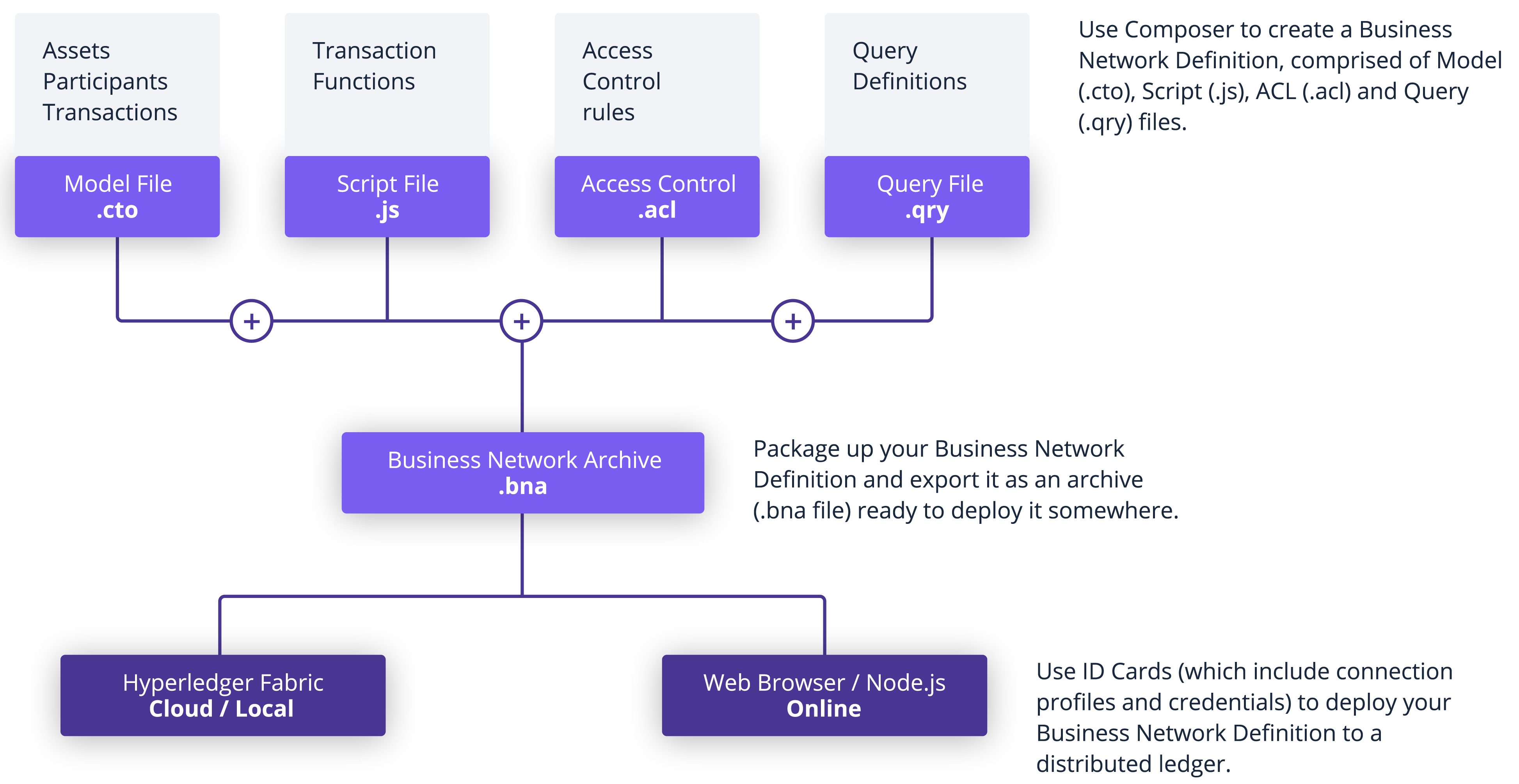
For typical solution architecture, refer to this link.
- Click Deploy a new business network under the Web Browser heading to get started.
Note: Do not click the Deploy a new business network under the heading Connection: hlfv1.
-
In Basic Information, name the network tutorial-network and optionally add a description.
-
In Model Network Starter Template, select the empty-business-network card. You will be building a business network from scratch.
-
Keep the rest of the default settings and click Deploy.
You should see a new business network card called admin for the business network tutorial-network in your wallet. The wallet can contain business network cards to connect to multiple deployed business networks.
When connecting to an external blockchain, business network cards represent everything necessary to connect to a business network. They include connection details, authentication material, and metadata.
- Now that the business network is deployed, click Connect now on tutorial-network.
Add a model file
You are now on the Define tab now. This is where you create and edit files that make up the business network definition.
Since you selected an empty business network template, you need to modify the default template files provided. The first step is to update the Model File. Model files define the assets, participants, transactions, and events in your business network.
-
Click Model File to view it.
-
Delete the existing lines of code in the Model File and replace it with this:
/**
* My commodity trading network
*/
namespace org.example.mynetwork
asset Commodity identified by tradingSymbol {
o String tradingSymbol
o String description
o String mainExchange
o Double quantity
--> Trader owner
}
participant Trader identified by tradeId {
o String tradeId
o String firstName
o String lastName
}
transaction Trade {
--> Commodity commodity
--> Trader newOwner
}
This domain model defines a single asset type Commodity and single participant type Trader and a single transaction type Trade that is used to modify the owner of a commodity.
Add a transaction processor script file
You can now define the transaction logic for the business network. Composer expresses the logic for a business network using JavaScript functions. These functions are automatically executed when a transaction is submitted for processing.
-
In the bottom left, click the Add a file link.
-
Click the Script File radio button, then Add.
-
Delete the lines of code in the script file and replace it with the following code:
/**
* Track the trade of a commodity from one trader to another
* @param {org.example.mynetwork.Trade} trade - the trade to be processed
* @transaction
*/
async function tradeCommodity(trade) {
trade.commodity.owner = trade.newOwner;
let assetRegistry = await getAssetRegistry('org.example.mynetwork.Commodity');
await assetRegistry.update(trade.commodity);
}
This function changes the owner property on a commodity based on the newOwner property on an incoming Trade transaction. It then persists the modified Commodity back into the asset registry, used to store Commodity instances.
Deploy the updated business network
Now that you have the model, script, and access control files, you can deploy and test your business network.
Click Deploy changes to upgrade the business network.
Test the business network definition
Next, test your business network by creating some participants (in this case Traders), creating an asset (a Commodity), and then using your Trade transaction to change the ownership of the Commodity.
Click the Test tab to get started.
Create participants
- Ensure that you have the Trader tab selected on the left, and click Create New Participant in the upper right.
- What you can see is the data structure of a Trader participant. We want some easily recognizable data, so delete the code that’s there and paste the following:
{
"$class": "org.example.mynetwork.Trader",
"tradeId": "TRADER1",
"firstName": "Jenny",
"lastName": "Jones"
}
-
Click Create New to create the participant.
-
You should be able to see the new Trader participant you created. You’ll need another Trader to test your Trade transaction though, so create another Trader, but this time, use the following data:
{
"$class": "org.example.mynetwork.Trader",
"tradeId": "TRADER2",
"firstName": "Amy",
"lastName": "Williams"
}
Make sure that both participants exist in the Trader view before moving on.
Create an asset
Now that you have two Trader participants, you need something for them to trade. Creating an asset is very similar to creating a participant. The Commodity you are creating will have an owner property indicating that it belongs to the Trader with the tradeId of TRADER1.
-
Click Commodity under Assets and click Create New Asset.
-
Delete the asset data and replace it with the following:
{
"$class": "org.example.mynetwork.Commodity",
"tradingSymbol": "ABC",
"description": "Test commodity",
"mainExchange": "Euronext",
"quantity": 72.297,
"owner": "resource:org.example.mynetwork.Trader#TRADER1"
}
- After creating this asset, you should be able to see it in the Commodity page.
Transfer commodity between participants
With two Traders and a Commodity to trade between them you can test your Trade transaction. Transactions are the basis of all changes in a Hyperledger Composer business network.
-
Click the Submit Transaction button on the bottom left.
-
Ensure that the transaction type is Trade.
-
Replace the transaction data with the following, or just change the details:
{
"$class": "org.example.mynetwork.Trade",
"commodity": "resource:org.example.mynetwork.Commodity#ABC",
"newOwner": "resource:org.example.mynetwork.Trader#TRADER2"
}
-
Click Submit.
-
Check that the asset has changed ownership from TRADER1 to TRADER2 by expanding the data section for the asset. You should see that the owner is listed as: org.example.mynetwork.Trader#TRADER2.
To view the full transaction history of the business network, click All Transactions on the left.
You will get a list of each transaction as they were submitted. You can see that certain actions performed using the UI, like creating the Trader participants and the Commodity asset, are recorded as transactions even though they are not defined as transactions in the business network model. These transactions are known as System Transactions and are common to all business networks and defined in the Hyperledger Composer Runtime.
In this lab, you created a business network from scratch and defined a model file inside it. Alternatively, you could deploy one of the sample networks available from Hyperledger.
Integrating with existing applications
Hyperledger Composer can be integrated with existing systems by using a Loopback API. Integrating existing systems allows you to pull data from existing business systems and convert it to assets or participants in a Composer business network.